Building Loading – Wind Load
(Revised: 10/14/2025)
The Wind Load tab defines design-related
information regarding the building(s) Wind Load.
The Wind loads are applied to the entire building, considering
all applicable Wind load options.
„
Note to
Builder/Customer:
The builder is responsible for contacting
the local building official or project design professional to obtain and
provide all code and loading information for the specific building site. Data supplied is assumed to be accurate.
Wind Load Information:
Wind Load
This
edit box is used to define the Wind load for the building. This load can be measured in Miles per Hour
(English - Speed or Velocity) or Pounds per Square Foot (English - Pressure)
based on the corresponding radio button selected.
Wind causes pressures and suctions on wall and roof
surfaces of buildings. The Wind load is
specified in the required building code.
Some building codes specify Wind velocity in MPH, while others specify
the resulting Wind pressure in PSF.
Sometimes specifications or local building departments will require more
severe Wind loads than those given in the code.
„
Note:
The Canadian codes and
some international codes require input of the Wind load as a Pressure value and
the Speed radio button is grayed out.
Speed
Select
the Speed option if entering the wind load as a wind velocity. This option measures the Wind velocity in
miles per hour (English). The software
converts the Wind speed to an equivalent Wind pressure based on the Building
Code requirements. External and internal
Wind coefficients are applied to the converted Wind pressure loads depending on
the building code selected.
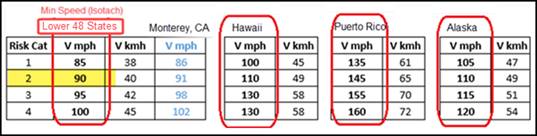
The
software enforces a Minimum Wind Speed for IBC codes and the Pressure radio
button is grayed out. The
minimums shown in the table below are enforced for IBC 2018 and reflects minimums for the entire Unites States; the actual
required Wind Speed may be higher and must be based on the Wind maps published
by the applicable building code.
Pressure
Select
the Pressure option if entering the Wind load as a Wind pressure. This option measures the Wind pressure in
Pounds per Square Foot (English units).
External and internal wind coefficients will be applied to the user
entered Wind pressure loads depending on the building code selected.
Use ‘All Heights’ Method (aka Directional Procedure)
When
the limits of Low-rise buildings given in ASCE 7-05 Section 6.2 (for 2006/2009
IBC), in ASCE 7-10 Section 26.2 (for 2012/2015 IBC), and in ASCE 7-16 Section
26.2 (for 2018/2021 IBC) are exceeded, or when selected by the user, Wind loads
will be calculated using the provisions for the rigid buildings of “All
Heights”. The “All Heights” method may
be used for any building height or configuration. This check box is not active for NBCC codes.
The
“All Heights” method is mandatory for Eave heights > 60 feet, and with
buildings with an eave height > the least horizontal dimension of the
building. The Wind load method will
automatically be selected by the software based on the building geometry. (The
“Low-rise” method is the default unless “All Heights” is required.) A switch can be made manually from Low-rise
to All Heights; however, the “All Heights” box cannot be unchecked if the
software determines that “All Heights” is required. Buildings using Wind Enclosure of “Open – All
Heights” will inherently be loaded with the “All Heights” method.
BBNA considers that
mezzanines prevent the use of the flexible diaphragm status and thus does not
permit the ASCE 7 Appendix Exception D.2.
Wind Exposure
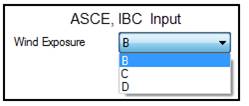
This
drop list defines the surrounding terrain of the building. Depending on the building code, the Wind
Exposure option may be disabled if it is not required by the code.
The Wind Exposure is used to recognize the impact
of the surrounding terrain during the calculation of the Wind pressure applied
to the building for the specified Wind velocity.
Wind Exposure
Descriptions:
![]() IBC 2021/2018 (ASCE 7-16), IBC 2015/IBC 2012
(ASCE 7-10), 2015 MNBC, 2020/2017 FL–HVHZ
IBC 2021/2018 (ASCE 7-16), IBC 2015/IBC 2012
(ASCE 7-10), 2015 MNBC, 2020/2017 FL–HVHZ
![]() ASCE 7-05, 2006 IBC, 2009 IBC, MAST (7th),
MAST (8th), 2018/2014 WICBC
ASCE 7-05, 2006 IBC, 2009 IBC, MAST (7th),
MAST (8th), 2018/2014 WICBC
![]() 2005 NBCC, 2010 NBCC, 2015 NBCC
2005 NBCC, 2010 NBCC, 2015 NBCC
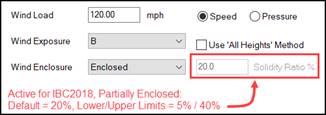
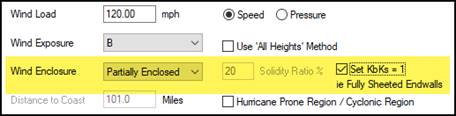
Wind Enclosure / Solidity Ratio %
|
|
|
|
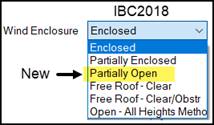
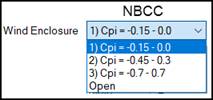
From this drop list, select the Wind Enclosure that
best describes the building – review the flow charts found in the “Levels of Wind Enclosure…” link, and/or
seek Engineering Assistance if unsure.
This option determines the net Wind loading on a building depending on
the presence of permanent Framed Openings or Wall Openings. Wind pressures for a Partially Enclosed
building are higher than those for an Enclosed building. Since each building code has its own definitions for Wind
Enclosure; reference the applicable building code. The Solidity Ratio % field is active
for IBC 2018 with Partially Enclosed input only; seek Engineering Assistance
when IBC 2018 Partially Enclosed is applicable for your building.
![]() Levels of Wind Enclosure
IBC 2021/2018 (ASCE 7-16)
Levels of Wind Enclosure
IBC 2021/2018 (ASCE 7-16)
![]() Levels of Wind Enclosure
IBC 2015 and older (ASCE 7-10), MAST (9th), MAST (8th),
2018/2014 WICBC, 2020/2015 MNBC,
2020/2017 FL–HVHZ
Levels of Wind Enclosure
IBC 2015 and older (ASCE 7-10), MAST (9th), MAST (8th),
2018/2014 WICBC, 2020/2015 MNBC,
2020/2017 FL–HVHZ
![]() Levels of Wind Enclosure
2005 NBCC, 2010 NBCC, 2015 NBCC
Levels of Wind Enclosure
2005 NBCC, 2010 NBCC, 2015 NBCC
„
Notes:
The User must set the Wind Enclosure as the system will NOT determine this condition. Contact a Service Center for engineering
assistance.
Regional Information:
Distance to the Coast
This
edit box is enabled when required by specific Building Codes. Enter the actual mileage to the nearest
coastline if less than 101 miles. Enter
101 miles when the distance from project to the coast exceeds 100 miles.
Building Base Elevation
In
this edit box, enter the height of the finished floor (typical base of columns)
above the ground elevation. This input
DOES affect the Wind loading on the building. This Building Base Elevation
dimension is commonly or normally thought of as 0'-0''.
Sample Conditions where the Building Base Elevation
might be revised:
1) To specify a floor elevation
change between building shapes
2) For a penthouse or cupola shape that will actually be on top of another shape
3) When the building or shape actually
sits on a concrete wall / elevated foundation, for example: a truck dock
terminal where the ground or grade elevation is several feet lower than the
base of the building columns (finish floor)
„
Note: This is NOT the actual (or the nominal 100'-0) elevation from sea
level designated as Fin. Fl. Elev. on the Geometry / Shape tab. If the 100/0/0 default elevation from sea
level / ground elevation is revised on the Geometry / Shape tab, the Wind load
will NOT be affected.
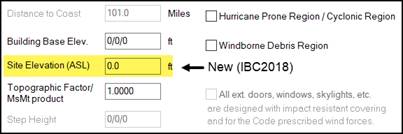
Site Elevation (ASL)
In
this edit box, enter the Site Elevation (Above
Sea Level) applicable to the project.
The minimum and maximum permissible elevations that may be entered are
0.0 ft and 15,000.0 ft. As stipulated by
the building code, Wind pressures will reduce as the Site Elevation increases
above sea level, 0.0 ft. The job site
examples shown below, indicates
that the Site Elevation for the city of Denver, CO is 5300.0 ft which will
reduce the wind pressure (loading) on the building by 17% when entered in the
Site Elevation field. This reduction can
reduce the price of a building to the extent that Wind loads control the
building design.

Topographic Factor / MsMt
This box is dual purpose and will typically be used for the Topographic Factor as described below. MsMt value is used by International Codes.
The Topographic Factor (Kzt
for IBC / ASCE based codes; Ct for 2015 NBCC) is a Wind load related coefficient that
increases the design Wind loads (Velocity Pressure) to account for localized,
job-site topographic features, such as isolated hills, ridges and escarpments
(in any Exposure Category) where there is an abrupt change in the general
topography that could cause a sudden change of the Wind speed. Contact a Service Center Engineer for help
with the appropriate factor if the building is located on or near a hill, ridge
or escarpment.
The default Topographic
Factor in the software is 1.0000. Please see the following for rare conditions
where this is unconservative.
For IBC or other standards
where Wind loads are calculated in accordance with ASCE 7, (Kzt)
must be evaluated and calculated for rare cases only, where all five
requirements listed below (Section 26.8.1, ASCE 7-16) are satisfied:
1.
H is greater than or equal to 15 feet (4.5 m) for
Exposures C and D and 60 feet (18m) for Exposures A and B.
2.
H/Lh >= 0.2, where:
Lh is distance upwind of crest
to where the difference in ground elevation is half the height of hill or
escarpment, in feet (meters).
H = Height of hill or escarpment relative to the
upwind terrain, in feet (meters).
3.
The hill, ridge, or escarpment is isolated and unobstructed upwind by
other similar topographic features of comparable height for 100 times the
height of the topographic feature (100*H)
or 2 miles (3.22 km), whichever is less.
This distance shall be measured horizontally from the point at which the
height H of the hill, ridge, or
escarpment is determined.
4.
The hill, ridge, or escarpment protrudes above the height of upwind
terrain features within a 2 mi (3.22 km) radius in any quadrant by a factor of
two or more.
5.
The structure is located as shown in Fig. 26.8-1 (ASCE 7-16) in the
upper one-half of a hill or ridge or near the crest of an escarpment.
When required, the Kzt
factor is calculated per Equation 26.8-1 (ASCE
7-16). In all other cases, Kzt
= 1.0000.
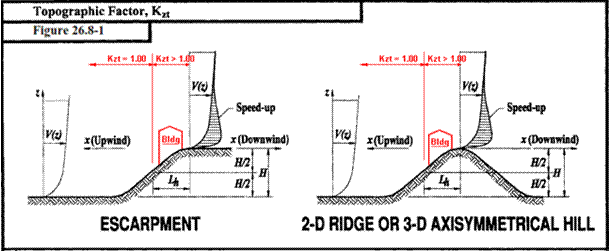
„ Note:
New in 2015 NBCC, the Topographic Factor, Ct, is defined per
Article 4.1.7.4. Similar
to Kzt above, Ct must be evaluated and calculated
for rare cases only for buildings situated at or near the tops of isolated
hills, ridges, and escarpments. When
required, the Ct factor is calculated per Article 4.1.7.4. In all other cases, Ct = 1.0000.
Step Height
This
edit box is intended for use with International Codes.
Hurricane Prone Region
This
Check Box should be selected when the project is located in
a Hurricane Prone Region as defined by the building code. By clicking in the box, the system will use
the appropriate Wind Importance Factor.
This check box is not active for NBCC codes.
„
Note:
If Hurricane Prone Region / Cyclonic
Region box is checked with a Building Use / Importance / Risk Category of Low
Hazard: Ag,
Storage, Temp selected, then the Wind Importance factor, Iw, will be reduced to 0.87 for winds up to 100 mph, and
reduced to 0.77 for winds greater than 100 mph when using ASCE 7-05 (Table
6-1). This check box is only valid for
IBC 2009 and older based codes; newer codes than IBC 2009 will have the check
box grayed out.
Windborne Debris Region
Coastal
region defined by the building code.
Verify with the local building code official, if applicable, for each
project. This check box is not active
for NBCC codes.
„
Notes:
If Windborne Debris Region is
applicable, see option for “All ext. doors, windows, skylights, etc.”
following.
Per 2014 FL–HVHZ
(5th) and newer for Broward and Miami-Dade counties in Florida, all buildings
fall within the Windborne Debris Region.
All Exterior Doors, Windows, etc.
If
the project is located in a Windborne Debris Region,
building shall be designed as a Partially Enclosed structure unless this radio
button is activated. Checking this box
indicates that you validate all doors and windows meet the design code criteria
for the building/shape to be considered Enclosed. This check box is not active for NBCC codes.
Regional Information:
Temp
Correction / Dom Opening Ratio
This
edit box is intended for use with International Codes.
Typhoon
This
edit box is intended for use with International Codes.
Normal
This edit box is intended for use by International
Codes.
Standard
Controls:
See also:
§
Building Loading - Building Codes
§
Building Loading - Live Load
§
Building Loading - Snow Load
§
Building Loading - Seismic Load
§
Building Loading - Tornado Load
§
Building Loading - Rain Load
§
Building Loading - Deflection Conditions